Data science has become one of the most in-demand and well-paid careers in today’s digital economy. From tech companies and startups to healthcare, finance, marketing, and government organisations, businesses rely on data scientists to turn raw data into meaningful insights that drive smarter decisions.
If you’re wondering how to become a data scientist, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from required skills and education to career paths, interview preparation, and how to break into the field with no degree or prior experience.
This step-by-step guide is designed for:
- Students planning a career in data science
- Working professionals considering a career switch
- Beginners with no technical background
- Anyone curious about how long it takes to become a data scientist and whether it’s the right career choice
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear roadmap to start and grow a successful career in data science.
Table of Contents
What Is a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is a professional who collects, analyses, and interprets large volumes of structured and unstructured data to solve complex business problems. They combine programming, statistics, and domain knowledge to extract insights that help organisations make data-driven decisions.
Unlike traditional analysts who mainly focus on reporting and dashboards, data scientists work on predictive and prescriptive problems, answering questions like:
- What will happen next?
- Why did this happen?
- How can we improve future outcomes?
What does a Data Scientist do daily?
A data scientist’s daily responsibilities may vary by industry and company size, but typically include:
- Collecting and cleaning large datasets from multiple sources
- Analysing data using statistical and machine learning techniques
- Building predictive models and algorithms
- Visualising data and presenting insights to stakeholders
- Collaborating with engineers, analysts, and business teams
- Improving data quality and model performance over time
In many roles, communication is just as important as technical expertise. A great data scientist doesn’t just find insights; they explain them in a way decision-makers can understand and act on.
Data Scientist vs Data Analyst vs Machine Learning Engineer
These roles are often confused, but they serve different purposes:
- Data Analyst: Focuses on descriptive analysis, dashboards, and reports. Primarily answers “what happened?”
- Data Scientist: Uses advanced analytics and machine learning to answer “why did it happen?” and “what will happen next?”
- Machine Learning Engineer: Focuses on deploying and scaling machine learning models into production systems
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right learning path when planning how to become a data scientist.
Why Choose a Career in Data Science?
Data science is a long-term, future-ready career, not a short-term trend. With demand across industries like tech, finance, healthcare, and marketing, skilled data scientists enjoy high earning potential and career flexibility.
Research from leading educational platforms shows that data science continues to be one of the most sought-after career paths globally.
According to Coursera, data science roles involve transforming data into meaningful insights that drive decisions across industries like healthcare, finance, and technology (Coursera’s data science career guide).
Organisations generate massive amounts of data every day, and skilled professionals are needed to turn that data into value.
Demand for Data Scientists Across Industries
Data scientists are needed across almost every sector, including:
- Technology and software
- Finance and banking
- Healthcare and life sciences
- E-commerce and retail
- Marketing and advertising
- Manufacturing and logistics
According to Coursera’s data science career guide, a career in data science includes roles like data analyst, machine learning engineer, and senior specialist, all leveraging analytical and programming skills to drive business insights.
As businesses continue adopting AI and automation, the demand for data science professionals continues to rise globally.
Career Growth and Future Opportunities
One of the biggest advantages of choosing data science as a career is flexibility and growth. You can progress into roles such as:
- Senior Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- AI Specialist
- Data Science Manager
- Chief Data Officer
You can also specialise in areas like artificial intelligence, natural language processing, computer vision, or big data engineering as your experience grows.
For many professionals, data science offers a rare combination of:
- Intellectual challenge
- High earning potential
- Cross-industry opportunities
- Long-term career stability
Skills Required to Become a Data Scientist
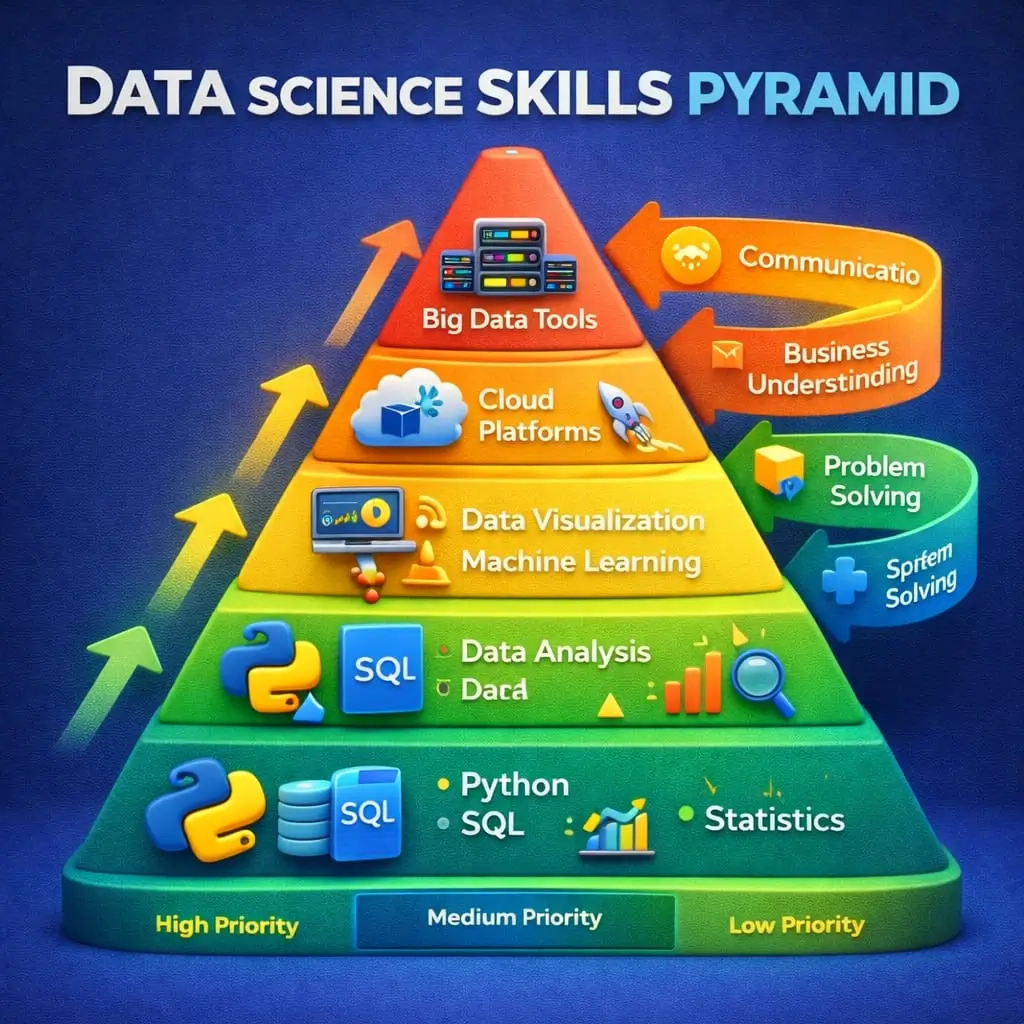
To become a successful data scientist, you need a balanced combination of technical expertise and soft skills. Many beginners make the mistake of focusing only on coding, but data science is as much about thinking and communication as it is about algorithms.
Community platforms like Kaggle offer practice environments where beginners can learn key data science skills and build project portfolios, an important part of data scientist qualifications.
You can also explore structured learning paths like the IBM Data Science Professional Certificate on Coursera, which covers Python, SQL, and data visualisation tools widely used by professionals.
Let’s break this down clearly.
Technical Skills Required for Data Science
These are the core technical skills employers expect when hiring data scientists.
Programming Languages for Data Science
The foundation of data science starts with programming.
- Python: The most widely used language for data science, machine learning, and AI
- R: Popular in statistics-heavy roles and academic research
- SQL: Essential for extracting and manipulating data from databases
👉 Python should be your first and topmost priority if you’re starting from scratch.
Statistics and Mathematics
Data science is built on statistical thinking. You don’t need a PhD, but you do need solid fundamentals.
Key topics include:
- Descriptive and inferential statistics
- Probability distributions
- Hypothesis testing
- Linear algebra basics
- Optimization concepts
Why this matters: Statistics helps you understand why a model works, not just how to build one.
Data Analysis and Visualisation
Before building models, data scientists spend a significant amount of time understanding data.
Important tools and skills:
- Data cleaning and preprocessing
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Visualisation libraries (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau, Power BI)
Being able to visually explain trends and patterns is crucial when presenting insights to stakeholders.
Machine Learning Basics
Machine learning allows data scientists to make predictions and automate decisions.
You should understand:
- Supervised vs unsupervised learning
- Regression and classification models
- Model evaluation metrics
- Overfitting and underfitting
You don’t need to master advanced algorithms early; strong fundamentals matter more than complexity.
Non-Technical Skills Every Data Scientist Needs
Many candidates overlook this, but non-technical skills are often the deciding factor in hiring.
Key soft skills include:
- Problem-solving mindset
- Business understanding
- Clear communication
- Storytelling with data
A great data scientist doesn’t just analyse data, they translate insights into business impact.
Skill Priority Table for Beginners
| Skill Area | Priority Level | Why It Matters |
| Python | High | Core language for data science |
| SQL | High | Used daily to access data |
| Statistics | High | Foundation of analysis and ML |
| Data Visualization | Medium | Communicating insights |
| Machine Learning | Medium | Predictive modeling |
| Big Data Tools | Low (Beginner) | Useful later, not day one |
Educational Pathways to Become a Data Scientist
One of the most common questions people ask is:
“Do I need a degree to become a data scientist?”
The short answer: No, but education still matters.
Do You Need a Degree to Become a Data Scientist?
Many data scientists come from traditional academic backgrounds, such as:
- Computer Science
- Statistics or Mathematics
- Engineering
- Physics or Economics
A degree can:
- Provide structured learning
- Help with early job opportunities
- Be useful for certain companies or regions
However, a degree is not mandatory if you can demonstrate skills through projects, experience, and a strong portfolio.
Best Universities for Data Science
For learners who prefer a structured academic route, choosing the right institution can make a difference.
Universities offer:
- Industry-recognized degrees
- Access to research and faculty
- Networking and internship opportunities
If you’re considering formal education, explore our detailed guide on the best universities for data science, including top global institutions and program comparisons
Education Path Comparison Table
| Pathway | Best For | Time Investment | Cost |
| University Degree | Students & fresh graduates | 3–4 years | High |
| Online Courses | Career switchers | 6–12 months | Low |
| Self-Learning | Self-motivated learners | Flexible | Very Low |
| Bootcamps | Fast-track learners | 3–6 months | Medium–High |
For a data science learning path that guides beginners from fundamentals all the way to job-ready skills, platforms like Coursera provide a clear learning roadmap that outlines essential topics, practical projects, and career preparation strategies.
Step-by-Step Roadmap: How to Become a Data Scientist
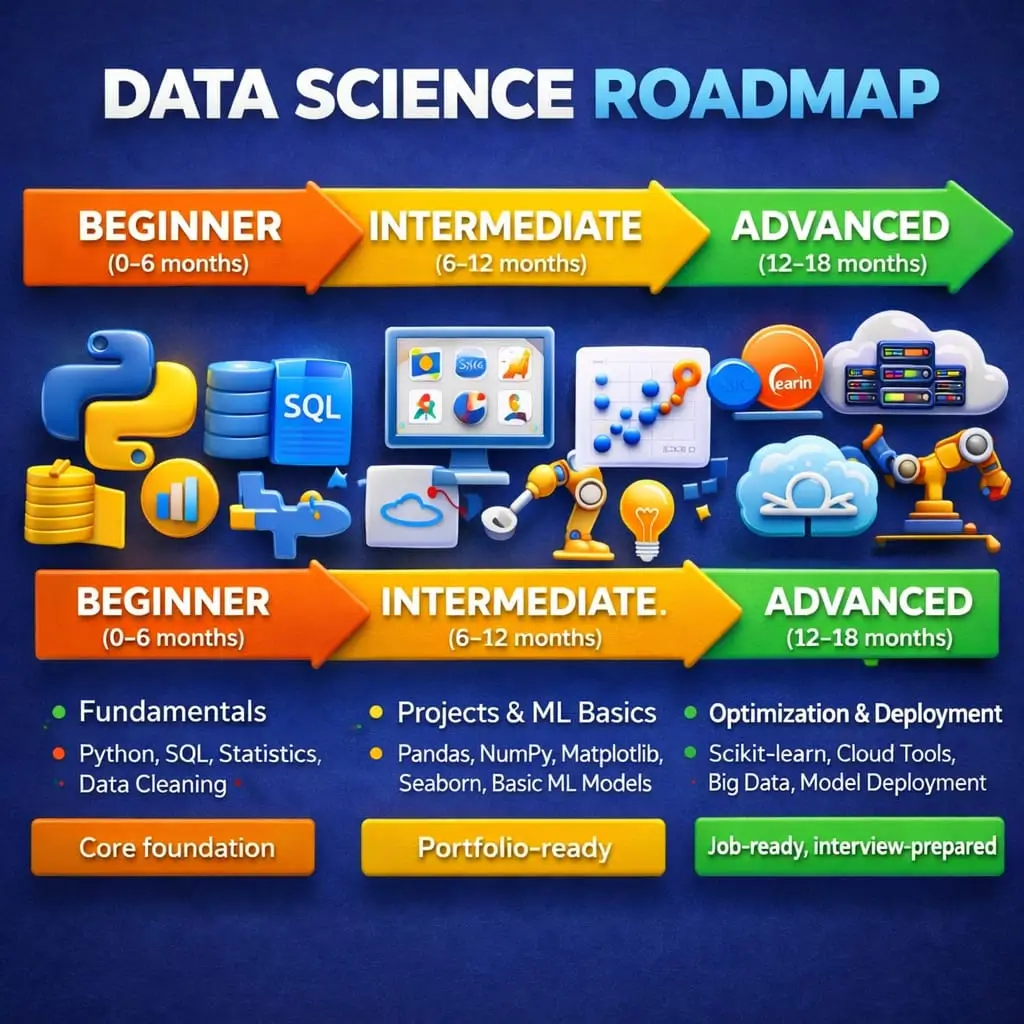
If you’re serious about becoming a data scientist, you need a clear, structured roadmap. Randomly watching tutorials won’t get you job-ready. This step-by-step path works whether you’re a student, career switcher, or complete beginner.
Step 1: Learn Data Science Fundamentals
Start with the foundations before jumping into advanced machine learning.
Focus on:
- Python programming (syntax, loops, functions, libraries)
- Statistics and probability basics
- SQL for data extraction
- Understanding datasets and data types
📌 Important: At this stage, consistency matters more than speed. Even 1–2 hours daily can compound quickly.
Step 2: Work on Real-World Data Science Projects
Projects are what separate learners from job-ready candidates.
Examples of beginner-friendly projects:
- Sales data analysis and forecasting
- Customer churn prediction
- Exploratory analysis on public datasets
- Recommendation systems (basic level)
Why projects matter:
- They prove you can apply concepts
- They replace “experience” on your resume
- They give you talking points for interviews
Step 3: Learn Data Science Tools and Technologies
Once fundamentals are clear, expand your toolkit.
Core tools:
- Python libraries: Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn
- Visualisation: Matplotlib, Seaborn
- Version control: Git & GitHub
- Databases: MySQL / PostgreSQL
Optional (later stage):
- Cloud platforms
- Big data tools
- Deployment basics
Step 4: Build a Strong Data Science Portfolio
Your portfolio is your proof of skill.
A strong portfolio should include:
- 4–6 well-documented projects
- Clean GitHub repositories
- Problem statements + solutions
- Visualisations and insights
📌 Recruiters care more about how you think than fancy algorithms.
Step 5: Apply for Data Science Jobs and Internships
Target roles such as:
- Junior Data Scientist
- Data Analyst (stepping stone)
- Machine Learning Intern
- Business Intelligence Analyst
Tailor your resume for each role and highlight:
- Projects
- Tools
- Measurable outcomes
Data Science Learning Roadmap Table
For a structured data science roadmap for beginners, platforms like Coursera explain how starting with statistics and programming before moving to projects and tools helps learners become job-ready in a systematic way.
| Stage | Focus | Outcome |
| Beginner | Python, stats, SQL | Core foundation |
| Intermediate | Projects, ML basics | Portfolio-ready |
| Advanced | Optimisation, deployment | Job-ready |
How to Become a Data Scientist With No Experience?
This is one of the highest-search questions, and the answer is absolutely yes, it’s possible.
Entry-Level Roles to Target First
Real-time labour market platforms like LinkedIn show many entry-level data scientist jobs available globally, including junior and analyst positions that serve as stepping stones into more advanced data science roles.
You don’t always need the “Data Scientist” title immediately.
Good starting roles:
- Data Analyst
- Junior Data Scientist
- Business Analyst
- Reporting Analyst
These roles help you gain hands-on experience with real business data.
How to Gain Experience Without a Job
If you have no professional experience:
- Build end-to-end projects
- Participate in Kaggle competitions
- Contribute to open-source projects
- Do freelance or internship work
Experience doesn’t have to be paid to be valuable; it has to be relevant and demonstrable.
Career Transition Tips for Non-Technical Professionals
If you’re switching from:
- Finance → focus on analytics + ML
- Marketing → focus on data visualisation + insights
- Operations → focus on optimisation + forecasting
Leverage your domain knowledge; it’s a major advantage.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Data Scientist?
Most beginners take 12 to 18 months to become job-ready for entry-level data science roles. The exact timeline depends on your background, learning pace, and the number of projects you complete.
Estimated Timeframe Table
| Background | Time Required |
| Technical degree | 6–12 months |
| Non-technical background | 12–18 months |
| Complete beginner | 18–24 months |
📌 With focused learning and projects, many learners land roles faster than expected.
Data Scientist Interview Preparation
Once you start applying, interview preparation becomes critical.
Data science interviews usually include:
- Technical questions
- Case studies
- Coding tasks
- Behavioral rounds
To prepare effectively, practice real-world questions used by employers.
Explore our curated list of data science interview questions to understand what top companies actually ask.
What Interviewers Look For
Interviewers evaluate:
- Problem-solving approach
- Understanding of fundamentals
- Ability to explain decisions
- Business thinking
It’s not about knowing everything, it’s about thinking clearly and logically.
Career Growth and Job Opportunities in Data Science
Data science offers long-term career flexibility.
Career Progression Path

- Junior Data Scientist
- Data Scientist
- Senior Data Scientist
- Lead / Manager
- AI or ML Specialist
Popular Specialisations
- Machine Learning Engineer
- AI Researcher
- Data Engineer
- NLP / Computer Vision Specialist
As your experience grows, you can specialise or move into leadership roles.
Challenges in Becoming a Data Scientist
While data science is a rewarding career, it is not without challenges. Understanding these early helps you prepare mentally and strategically.
Steep Learning Curve
Data science combines multiple disciplines, including programming, mathematics, and business thinking. Many beginners feel overwhelmed at the start.
How to overcome it
- Focus on fundamentals first
- Learn one tool or concept at a time
- Avoid comparing your progress with others
Lack of Real-World Experience
Many aspiring data scientists struggle with the experience requirement.
How to overcome it
- Build end-to-end projects that mimic business problems
- Use publicly available datasets
- Document your work clearly on GitHub
Recruiters value demonstrated problem-solving ability over job titles.
Keeping Up With Rapidly Changing Tools
The data science ecosystem evolves quickly.
How to overcome it
- Master core concepts instead of chasing every new tool
- Follow industry blogs and communities
- Continuously update your skills gradually
How to Become a Data Scientist Without a Degree?
Many data scientists enter the field without a formal degree by focusing on skills, proof of work, and business impact rather than credentials. Employers increasingly prioritise what you can do over where you studied.
1. Learn Core Data Science Skills (With a Clear Path)
Instead of “learning everything,” follow a focused skill roadmap:
Technical foundations
- Python: pandas, NumPy, matplotlib, seaborn
- SQL: joins, subqueries, window functions
- Statistics: probability, hypothesis testing, regression
- Machine Learning: scikit-learn, model evaluation, feature engineering
- Data Visualisation: storytelling with charts and dashboards
Action steps
- Follow structured courses (Coursera, DataCamp, freeCodeCamp)
- Practice daily on Kaggle and LeetCode (SQL problems)
- Rebuild small datasets end-to-end (from raw data → insights)
Pro tip: Document why you chose each method, not just the code.
2. Build Real-World Projects That Solve Problems
Projects are your substitute for a degree.
High-impact project ideas
- Predict customer churn using real business metrics
- Analyse sales data and recommend revenue improvements
- Build a recommendation system (movies, products, courses)
- Create a fraud detection or pricing optimisation model
Action steps
- Use real datasets (Kaggle, government portals, company APIs)
- Frame every project like a business case:
- Problem statement
- Data cleaning & assumptions
- Model choice & evaluation
- Business recommendations
Pro tip: One strong, well-documented project beats five shallow ones.
3. Create a Professional Portfolio That Shows Value
Your portfolio is your degree replacement.
What to include
- GitHub repositories with clean code and READMEs
- Jupyter notebooks explaining your thinking
- A personal website (GitHub Pages, Notion, or WordPress)
- Visual dashboards (Tableau, Power BI, Streamlit apps)
Action steps
- Write a short case study for each project
- Highlight outcomes: “Improved prediction accuracy by 18%”
- Add a short “What I’d improve next” section
Pro tip: Recruiters spend ~30 seconds scanning—make insights obvious.
4. Demonstrate Business Understanding (This Is Critical)
Data scientists are hired to make decisions better, not just build models.
Key business skills
- Translating data into recommendations
- Understanding KPIs and trade-offs
- Communicating results to non-technical stakeholders
Action steps
- Practice writing executive summaries
- Turn analyses into slide decks
- Study basic business concepts (marketing funnels, revenue models)
Pro tip: Always ask, “So what?” after every result.
How to Become a Data Scientist With No Experience
You don’t need prior professional experience; you need proof that you can do the work.
1. Start With Personal and Open-Source Projects
Treat self-directed work like a job.
Action steps
- Set weekly project deadlines
- Contribute to open-source data projects
- Participate in Kaggle competitions (focus on learning, not ranking)
Pro tip: Write blog posts explaining your approach—this builds credibility fast.
2. Apply for Internships and Entry-Level Roles Strategically
You’re not just applying, you’re positioning.
Target roles
- Data Analyst
- Business Analyst
- Junior Data Scientist
- Operations or Marketing Analyst
Action steps
- Tailor resumes to highlight skills + projects
- Quantify results from projects
- Apply even if you meet ~60% of the requirements
Pro tip: Many “entry-level” jobs are flexible on degrees but strict on skills.
3. Use Analyst Roles as Stepping Stones
Many data scientists started as analysts.
How to transition
- Volunteer for advanced analysis at work
- Introduce automation or ML into reports
- Ask for cross-team data projects
Pro tip: Internal transitions are often easier than external job hops.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Data Scientist?
The time required depends on your background and commitment.
| Background | Estimated Time |
| Technical background | 6 to 12 months |
| Non-technical background | 12 to 18 months |
| Complete beginner | 18 to 24 months |
Consistent practice and project-based learning can shorten this timeline significantly.
Is Data Science a Good Career Choice?
Data science is a strong career choice if you:
- Enjoy problem-solving
- Are comfortable working with data
- Like continuous learning
- Want cross-industry opportunities
It may not be ideal if you prefer repetitive tasks or avoid analytical thinking.
Can Non-Technical Professionals Become Data Scientists?
Yes. Many successful data scientists come from finance, marketing, operations, and economics backgrounds. Domain knowledge combined with data skills is a powerful advantage.
Is Data Science the Right Career for You?
Data science is ideal for people who enjoy turning information into insights. If you are curious, analytical, and willing to invest time in learning, this career can be highly rewarding.
However, success requires patience. Mastery does not happen overnight, but steady progress leads to strong long-term results.
If you prefer structured thinking, real-world problem solving, and continuous growth, data science is worth pursuing.
Becoming a data scientist is not just a career choice; it is a strategic investment in a future-ready profession. The journey involves building foundational skills, practising with real-world projects, developing a strong portfolio, and preparing effectively for interviews.
Key takeaways:
- Yes, you can become a data scientist without a degree. Focus on self-learning, practical projects, and online courses to demonstrate skills.
- No, prior professional experience is not mandatory. Entry-level roles like Data Analyst or Junior Data Scientist provide on-the-job learning.
- Most beginners take 12 to 18 months to become job-ready, depending on background and learning pace.
- Data science is a long-term, future-ready career, offering high earning potential, intellectual challenge, and cross-industry flexibility.
Next Steps:
- Explore our guide on the best universities for data science for formal education pathways.
- Practice with our curated data science interview questions to ace hiring processes.
- Start building a portfolio on platforms like GitHub or Kaggle to showcase your skills.
- Follow industry-leading resources, such as Coursera’s data science career guide and IBM’s data science report, to stay updated with trends and skills in demand.
By following this structured roadmap, anyone, whether a complete beginner or a professional looking to switch careers, can successfully enter and thrive in the data science field. Consistency, project-based learning, and a clear career plan are the keys to success.
FAQs
What does a Data Scientist actually do?
A Data Scientist collects, cleans, analyses, and interprets large amounts of data to solve business problems. They use statistics, programming, and machine learning to find patterns and help organisations make data-driven decisions.
What skills are required to become a Data Scientist?
To become a Data Scientist, you need a combination of technical and analytical skills. These include programming in languages such as Python or R, a strong understanding of statistics and mathematics, experience with databases and SQL, knowledge of machine learning techniques, and the ability to explain insights in a clear and meaningful way.
Is a university degree necessary to become a Data Scientist?
A university degree can be helpful, but it is not always essential. Many Data Scientists come from diverse educational backgrounds. Employers often focus more on practical skills, real-world projects, problem-solving ability, and a strong portfolio than on formal qualifications alone.
How long does it take to become a Data Scientist?
The time required depends on your starting point. For someone with no prior experience, it may take around nine to eighteen months of consistent learning and practice. Those with a background in programming, mathematics, or analytics may be able to transition in a shorter period.
Which tools and technologies should I learn first?
Beginners should focus on learning Python, data analysis libraries such as Pandas and NumPy, SQL for working with databases, and basic machine learning concepts. Familiarity with tools like Jupyter Notebook and version control systems such as Git is also important.
How can I gain experience without a job in Data Science?
You can gain experience by working on personal projects using real datasets, taking part in online competitions, completing internships, or contributing to open-source projects. Sharing your work on platforms like GitHub or writing about your projects can also help demonstrate your skills.
Is Data Science a good career choice?
Data Science is considered a strong career option due to high demand across many industries, competitive salaries, and growth opportunities. As data continues to play a central role in decision-making, skilled Data Scientists are likely to remain in demand in the future.

Content Strategist | AI Tools Practitioner | Career & Study Abroad Consultant
Sagar Hedau is a content strategist and AI tools practitioner based in Nagpur, India. With 13+ years of experience in career counselling and psychometry, he now works at the intersection of content strategy and no-code AI technology, using tools like Claude, Lovable, LovArt, and Notion AI in his daily workflow. He writes to make AI genuinely accessible for non-technical professionals, students, and business owners who want to build and automate without coding. He also runs an active career counselling practice, helping individuals navigate career decisions with data-backed psychometric analysis.
🌐 sagarhedau.com | 💼 LinkedIn

