Business Analyst? Ye kya hota hai? Kya kaam karta hai? Kuch karta bhi hai ya nahi?
In today’s evolving business landscape, organisations across India are increasingly recognising the critical importance of data-driven decision-making. At the heart of this transformation stands the business analyst, a professional whose diverse skillset bridges the gap between business objectives and technological solutions.
But what exactly does a business analyst do? What is the role of a business analyst in an organisation? And why has this role become indispensable for companies seeking a competitive edge? This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted role of business analysts, their day-to-day responsibilities, and the tremendous value they bring to modern organisations.

What Is a Business Analyst? The Strategic Connector
A business analyst (BA) serves as the crucial link between stakeholders and the technical team, translating business needs into functional requirements that drive technological solutions.
Far more than just data interpreters, today’s business analysts are strategic advisors who help organisations navigate complex challenges, identify opportunities for improvement, and implement changes that deliver measurable business value.
According to a 2024 survey by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), organisations with dedicated business analysts report 32% higher project success rates compared to those without.
This statistic underscores the pivotal role these professionals play in ensuring projects deliver their intended benefits and align with broader organisational goals.
Why should you consider becoming a Business Analyst?
- Strong Job Demand and Security
Business analyst roles are in high demand across industries due to the growing need for data-driven decision-making and process optimisation. This demand translates into excellent job security and a wide range of opportunities in sectors like IT, healthcare, finance, and more. - Competitive Salary and Benefits
Business analysts enjoy above-average wages, with competitive salaries, performance-based bonuses, and attractive benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. This financial stability is a key draw for many professionals. - Intellectual Challenge and Variety
The role offers constant new challenges, as business analysts tackle diverse projects and solve complex problems. This keeps the work engaging and helps avoid monotony. - High Level of Independence and Autonomy
Business analysts often have the freedom to set their own schedules, approach problems creatively, and make impactful decisions, leading to a high degree of professional autonomy. - Direct Impact on Business Success
Business analysts play a crucial role in improving business processes, reducing costs, and driving organisational success. Their work leads to measurable improvements that benefit both the company and its employees. - Opportunities for Professional Growth
The field encourages continuous learning and skill development, offering clear paths for advancement to senior or management roles. Business analysts often gain interdisciplinary knowledge, making them valuable across multiple business functions. - Collaboration and Networking
Business analysts regularly interact with stakeholders from various departments, fostering collaboration and expanding professional networks. Opportunities to attend conferences and industry events further enhance networking potential. - Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Many business analyst positions offer flexible working hours and the possibility of remote work, supporting a healthy work-life balance. - Prestige and Recognition
The role is respected within organisations, as business analysts are seen as key contributors to strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. - Personal Fulfillment
Helping organisations and colleagues work more efficiently and seeing the tangible results of your efforts can be highly rewarding and motivating.
Is Business Analyst a good job profile?
Yes, being a Business Analyst is generally considered a good job profile for several reasons:
- Strong Demand and Career Growth: Business analysts are in high demand across industries like IT, finance, and consulting. With experience, they can progress to managerial roles or specialise in areas such as data analytics and project management.
- Competitive Salary: Salaries for business analysts in India range broadly, often from ₹14 lakhs to ₹43 lakhs per year, depending on experience, skills, and industry, making it a financially rewarding career.
- Job Satisfaction: Many business analysts find intellectual stimulation in their work, enjoy the opportunity to make a tangible impact, and appreciate flexible work environments, including options for remote work.
- Meaningful Work: Business analysts help improve business processes, reduce costs, and bridge the gap between technology and business goals, which can be fulfilling.
- Work Environment: The role offers a mix of collaborative and independent work, often in dynamic corporate or startup settings.
- Challenges and Stress: While the job can be challenging, it is not overwhelmingly stressful if approached with the right mindset and support.
However, some surveys indicate that business analysts rate their overall career happiness moderately (around 3.0 out of 5), with mixed feelings about the meaningfulness of their work. Personality fit and skills utilisation tend to be rated higher, suggesting that success and satisfaction depend on individual preferences and how well one adapts to the role.
What is the role of a business analyst in an organisation? 7 Key Roles
1. Requirements Gathering and Analysis
The foundation of a business analyst’s work begins with thoroughly understanding what the business needs. This involves:
- Conducting stakeholder interviews and workshops
- Documenting business requirements
- Creating user stories and use cases
- Performing gap analysis between the current and desired states
Effective requirements gathering prevents costly misunderstandings and ensures that solutions address the actual business problems rather than symptoms.
2. Process Optimisation and Improvement
Business analysts are experts at identifying inefficiencies and recommending process improvements. Using methodologies such as Six Sigma, Lean, and Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN), they:
- Map existing processes to identify bottlenecks
- Recommend streamlined workflows
- Quantify potential savings from process improvements
- Facilitate change management initiatives
A recent McKinsey report found that Indian companies that invested in business process optimisation achieved cost reductions of 15-25% while simultaneously improving service quality.
3. Data Analysis and Interpretation
In our data-rich environment, business analysts transform raw information into actionable insights by:
- Collecting and cleaning data from multiple sources
- Performing statistical analysis to identify trends
- Creating visualisations that communicate complex findings
- Translating data insights into business recommendations
This data-driven approach enables organisations to make decisions based on evidence rather than intuition, significantly improving outcomes across all business functions.
4. Stakeholder Communication and Management
Business analysts serve as translators between technical teams and business stakeholders, ensuring all parties share a common understanding. This critical communication function involves:
- Facilitating meetings between diverse stakeholders
- Managing expectations and resolving conflicts
- Presenting complex technical concepts in business-friendly language
- Maintaining ongoing communication throughout project lifecycles
By bridging communication gaps, business analysts help prevent the misalignments that can derail even the most promising initiatives.
5. Solution Evaluation and Testing
Before implementation, business analysts evaluate proposed solutions to ensure they meet business requirements by:
- Developing test plans and test cases
- Participating in user acceptance testing
- Validating that solutions address the original business needs
- Identifying and documenting defects for resolution
This quality assurance function helps prevent costly implementation failures and ensures solutions deliver their intended benefits.
6. Change Management and Implementation Support
Successfully implementing new solutions requires more than technical expertise—it demands careful attention to the human elements of change. Business analysts support this process by:
- Creating implementation roadmaps
- Developing training materials and documentation
- Supporting users during transition periods
- Measuring adoption rates and addressing resistance
According to PwC India, projects with robust change management support are six times more likely to meet their objectives than those without.
7. Continuous Improvement and ROI Analysis
The business analyst’s role doesn’t end with implementation. These professionals continue to:
- Monitor solution performance against key metrics
- Identify opportunities for further improvements
- Calculate the return on investment for implemented changes
- Make recommendations for future initiatives
This ongoing evaluation ensures that organisations continue to derive maximum value from their investments.
The Business Analyst Toolkit: Essential Skills and Techniques
Effective business analysts combine technical knowledge with business acumen and interpersonal skills. Their toolkit typically includes:
- Technical Skills: Data analysis, SQL, requirements modelling, process mapping, and familiarity with project management methodologies
- Business Knowledge: Understanding of business operations, industry trends, financial principles, and strategic planning
- Soft Skills: Communication, critical thinking, problem-solving, negotiation, and facilitation
In the Indian context, business analysts also need cultural sensitivity and awareness of local regulatory environments, particularly in sectors like finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
The Evolving Role of Business Analysts in Digital Transformation
As Indian organisations embrace digital transformation, the business analyst’s role continues to evolve. Today’s BAs are increasingly involved in:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning initiatives
- Data governance and compliance
- Customer experience optimisation
- Agile and DevOps implementation
A 2024 Gartner report indicates that 67% of Indian enterprises now consider business analysis skills essential for their digital transformation efforts, up from 45% just three years ago.
Business Analysts vs. Other Roles: Understanding the Differences
The business analyst role sometimes overlaps with other positions, causing confusion. Here’s how it differs:
- Project Managers: Focus on delivering projects on time and within budget; BAs focus on ensuring solutions meet business needs
- Data Scientists: Specialise in advanced statistical analysis and predictive modelling; BAs translate these insights into business applications
- Systems Analysts: Concentrate on technical system requirements; BAs emphasise business requirements and outcomes
Understanding these distinctions helps organisations build complementary teams with the right mix of skills and perspectives.
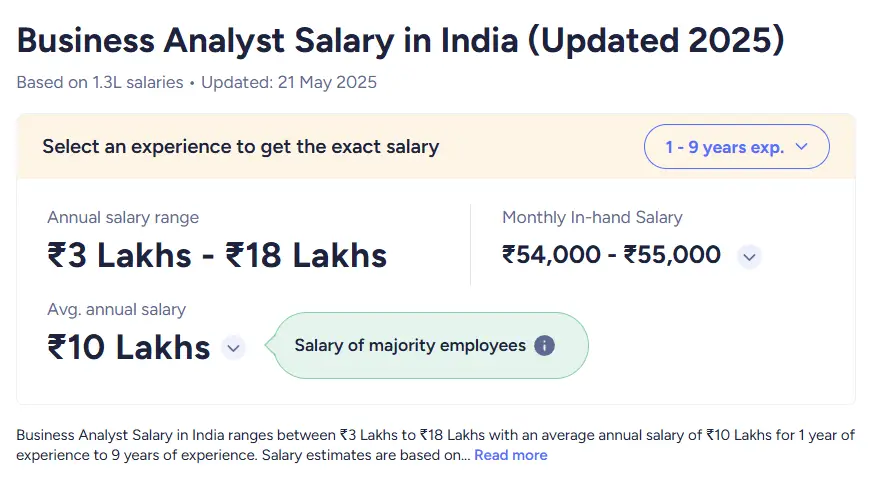
Business Analyst Salary Statistics in India (2025)
Average Salary
- The average annual salary for a Business Analyst in India is approximately INR 9 lakhs according to Glassdoor, with freshers earning around INR 7 lakhs and senior business analysts averaging INR 15 lakhs per year.
- Another large-scale salary aggregator reports a higher average of INR 17.1 lakhs per year, with most salaries ranging from INR 13.5 lakhs to INR 48.8 lakhs.
Salary by Experience
- Freshers: INR 6–7 lakhs per annum is typical for entry-level roles.
- Mid-level (4–6 years): Salaries can reach INR 8–13 lakhs per annum, with monthly averages up to INR 83,000.
- Senior Analysts (10+ years): Can earn upwards of INR 15–30 lakhs per annum, with top professionals earning significantly more.
- Top 10%: Earn more than INR 27 lakhs per year; the top 1% can earn over INR 48.8 lakhs per year.
Highest Salaries
- In top consulting firms, salaries can range from INR 10 lakhs to INR 1 crore, depending on experience and firm.
- The highest reported salary for a Business Analyst in India is INR 2.32 crore (INR 23.2 million).
Salary by Industry (Annual Averages)
| Industry | Average Salary |
|---|---|
| IT Services & Consulting | 9.5L |
| Management Consulting | 10.4L |
| Manufacturing | 10.8L |
| Fintech | 11.1L |
| FMCG | 10.6L |
| Emerging Technologies | 11L |
| Logistics | 11L |
Salary by Companies
| Company | Avg. Annual Salary | Experience Range | Salary Range (per year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCS | ₹9.1 Lakhs | 0 – 13 yrs (9.1k salaries) | ₹4 L – ₹15.6 L |
| Genpact | ₹8.3 Lakhs | 0 – 11 yrs (5.2k salaries) | ₹4 L – ₹13.2 L |
| Accenture | ₹9.9 Lakhs | 0 – 10 yrs (3.7k salaries) | ₹4.2 L – ₹17.7 L |
| Wipro | ₹10.6 Lakhs | 0 – 13 yrs (3k salaries) | ₹4.5 L – ₹18.1 L |
| Cognizant | ₹9.7 Lakhs | 0 – 13 yrs (2.7k salaries) | ₹1.8 L – ₹29.5 L |
| Capgemini | ₹11.3 Lakhs | 0 – 12 yrs (1.6k salaries) | ₹4.9 L – ₹19 L |
| Amazon | ₹14.2 Lakhs | 0 – 10 yrs (1.5k salaries) | ₹7 L – ₹25 L |
| Tech Mahindra | ₹10.4 Lakhs | 1 – 11 yrs (1.5k salaries) | ₹4.5 L – ₹17.5 L |
| Deloitte | ₹12.5 Lakhs | 1 – 9 yrs (1.4k salaries) | ₹5.5 L – ₹19.2 L |
| IBM | ₹16.3 Lakhs | 1 – 20 yrs (1.4k salaries) | ₹6.3 L – ₹26.3 L |
Conclusion: The Business Analyst as a Strategic Partner
So, what is the role of a business analyst in an organisation? Far more than technical specialists, today’s business analysts serve as strategic partners who help organisations navigate complex challenges and capitalise on emerging opportunities.
By bridging the gap between business needs and technical solutions, facilitating communication among diverse stakeholders, and ensuring that projects deliver measurable value, business analysts have become indispensable to modern enterprises.
For Indian organisations seeking to thrive in an increasingly competitive global marketplace, investing in skilled business analysts is not merely a tactical decision—it’s a strategic imperative that can dramatically improve project outcomes, operational efficiency, and bottom-line results.
Whether you’re considering a career as a business analyst or looking to strengthen your organisation’s analytical capabilities, understanding the multifaceted role these professionals play is the first step toward harnessing their transformative potential.
FAQs: What is the role of a business analyst in an organisation?
What qualifications do you need to become a business analyst in India?
Most business analysts have a bachelor’s degree in business, IT, or a related field. Professional certifications like IIBA-CBAP or PMI-PBA are increasingly valued, along with experience in relevant industries.
How much do business analysts earn in India?
Entry-level business analysts in India typically earn ₹4-6 lakhs annually, while experienced professionals can command ₹12-20 lakhs or more, with variation based on location, industry, and specialisation.
What’s the difference between a business analyst and a systems analyst?
Business analysts focus on business requirements and outcomes, while systems analysts concentrate more on technical specifications and system functionality.
Do business analysts need programming skills?
While not always required, basic programming knowledge can be beneficial. More important are analytical skills, business acumen, and the ability to understand technical concepts.
How are business analysts involved in agile projects?
In agile environments, business analysts often serve as product owners or work closely with them, managing the product backlog, refining user stories, and ensuring the team delivers business value.
What industries employ the most business analysts in India?
IT services, banking and financial services, healthcare, telecommunications, and e-commerce currently have the highest demand for business analysts in India.

13+ Yrs Experienced Career Counsellor & Skill Development Trainer | Educator | Digital & Content Strategist. Helping freshers and graduates make sound career choices through practical consultation. Guest faculty and Digital Marketing trainer working on building a skill development brand in Softspace Solutions. A passionate writer in core technical topics related to career growth.