As businesses continue to generate massive amounts of data, the need for professionals who can make sense of this information has become increasingly important. This is where data analysts come in. A data analyst is responsible for collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to help organizations make informed decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will demystify the data analyst roles and responsibilities, explore the importance of data analysis in businesses, and discuss the key skills and qualifications required to excel in this field.
Table of Contents
Importance of data analysis in businesses
In today’s data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on data analysis to gain a competitive edge. Data analysis allows organizations to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can drive strategic decision-making.
By analyzing data, businesses can optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and increase profitability. Data analysis also helps in identifying potential risks and opportunities, enabling organizations to stay ahead of the curve.
With the increasing availability of data, the role of data analysts has become crucial in extracting meaningful and actionable insights from the vast amount of information that businesses generate.
Key skills and qualifications required for a data analyst
Being a data analyst requires a diverse set of skills and qualifications. First and foremost, a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics is essential.
Data analysts need to be proficient in statistical analysis methods, mathematical modelling, and data visualization techniques. They should also have a solid understanding of programming languages such as Python or R, as these are commonly used for data analysis tasks.
Additionally, strong problem-solving and critical thinking skills are crucial for data analysts to effectively analyze complex datasets and draw meaningful conclusions.
Excellent communication skills are also important, as data analysts often need to present their findings to non-technical stakeholders clearly and concisely.
Data Analyst roles and responsibilities
Data analyst roles and responsibilities may vary depending on the organization and industry they work in. However, some common tasks and responsibilities include data collection, data cleaning and preprocessing, data analysis and interpretation, and reporting.
Data analysts are responsible for gathering data from various sources, organizing it in a structured manner, and ensuring its accuracy.
They then analyze the data using statistical techniques, identify trends and patterns, and present their findings in the form of reports or visualizations. Data analysts also play a crucial role in identifying areas for improvement and making data-driven recommendations to help businesses achieve their goals.
Skills To Execute Data Analyst roles and responsibilities
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Data analysts must possess the skills to meticulously clean and prepare datasets for analysis. This involves the systematic removal of errors, identification and handling of outliers, and transforming data into a structured format suitable for analytical purposes.
Data Analysis and Exploration
Proficiency in analyzing and exploring data is a crucial skill for data analysts. This entails the application of statistical methods to test hypotheses, discern trends, and formulate predictions based on the observed patterns within the dataset.
Statistical Analysis
A solid understanding of statistical tests and tools is imperative. Fundamental knowledge includes familiarity with measures such as mean, median, variance, and standard deviation, as well as competence in correlation, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
Programming
Mastery of programming languages is essential, particularly:
- Python: Proficiency in using libraries like pandas, Numpy, and Scikit-learn for data manipulation and analysis.
- R: Competence in leveraging R for statistical analysis and data visualization.
Database Management
The capability to query databases using SQL is a fundamental skill for extracting data. Familiarity with various database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, or MS SQL is also important.
Creating Dashboards and Reports
Data analysts must possess the ability to develop insightful dashboards and reports for effective communication with stakeholders. This involves utilizing tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Microsoft Word to create interactive and informative presentations.
Data Visualization
Proficiency in using visualization tools and libraries like Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib, Seaborn, or ggplot2 is essential. This skill enables analysts to represent complex data in a visual format that is easily understandable and aids in conveying insights.
Machine Learning
Given the growing significance of machine learning, data analysts should be adept at leveraging it for automation, pattern identification, and prediction tasks. Proficiency in machine learning allows analysts to harness advanced algorithms for enhanced data analysis.
Tools and software commonly used by data analysts
Data analysts rely on a wide range of tools and software to perform their tasks efficiently. Some commonly used tools include Microsoft Excel, SQL for database querying, and Python or R for data analysis and visualization.
- Microsoft Excel: Widely used for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. Offers spreadsheet functionality with a variety of built-in functions.
- SQL (Structured Query Language): Essential for database management and querying. Allows data analysts to extract, manipulate, and analyze data from relational databases.
- Python: A versatile programming language with numerous libraries (e.g., Pandas, NumPy) for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning.
- R: Statistical programming language used for data analysis, visualization, and statistical modeling. Preferred for its robust statistical packages.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that simplifies the creation of interactive and shareable dashboards, aiding in data exploration and presentation.
- Power BI: Business analytics tool by Microsoft for data visualization, sharing insights across an organization, and creating interactive reports and dashboards.
- Jupyter Notebooks: An open-source web application that allows the creation and sharing of live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text in a single document.
- SAS (Statistical Analysis System): Software suite for advanced analytics, business intelligence, and data management. Widely used in industries like finance, healthcare, and research.
- Apache Hadoop: Framework for distributed storage and processing of large data sets. Used for big data analytics and handling massive datasets.
- MATLAB: High-performance language for technical computing, often used for numerical analysis, algorithm development, and data visualization.
- Google Analytics: Web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic. Provides insights into user behavior and site performance.
- SAS Enterprise Miner: Data mining software for creating predictive and descriptive models. Used for tasks like clustering, decision trees, and regression analysis.
- Apache Spark: Open-source, distributed computing system for big data processing. Enables data analysts to perform complex analytics tasks efficiently.
- Alteryx: Data blending and advanced data analytics platform. Streamlines data preparation and cleansing tasks for analysis.
- QlikView: Business intelligence tool that allows data visualization, dashboard development, and interactive data exploration. Enables users to make data-driven decisions efficiently.
Data Analyst Specializations
- Medical and Healthcare Analyst
- Focus: Improving healthcare outcomes
- Scope: Utilizes data from various sources to enhance patient care and streamline medical operations.
- Market Research Analyst
- Focus: Consumer and competitor data analysis
- Scope: Investigate market conditions to project future product or service sales, aiding businesses in understanding customer preferences, target demographics, and pricing strategies.
- Business Analyst
- Focus: Enhancing corporate efficiency
- Scope: Utilizes data to derive business insights and recommend improvements in areas such as IT processes, organizational structures, and employee development.
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Focus: Supporting effective business decision-making
- Scope: Analyzes and visualizes data, including revenue, sales, market intelligence, and consumer engagement indicators, to assist firms in making informed strategic choices.
- Operations Research Analyst
- Focus: Efficient and cost-effective problem-solving
- Scope: Utilizes advanced techniques like optimization, data mining, statistical analysis, and mathematical modeling to provide solutions for improved operational efficiency.
- Intelligence Analyst
- Focus: Identifying and mitigating security concerns
- Scope: Analyzes internal and external data sources, including statistics, databases, and field reports, to synthesize information and develop action plans for security measures.
Top Companies Hiring Data Analysts
| Company | Industry |
|---|---|
| Technology | |
| Microsoft | Technology |
| Amazon | E-commerce/Technology |
| Social Media/Technology | |
| IBM | Technology/Consulting |
| Apple | Technology |
| Netflix | Entertainment/Streaming |
| Professional Networking/Technology | |
| Uber | Ride-sharing/Technology |
| PayPal | Finance/Technology |
Differences between data analyst, data scientist, and business analyst roles
While the roles of data analyst, data scientist, and business analyst may overlap to some extent, there are distinct differences between them. Data analysts focus primarily on collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to identify insights and make data-driven recommendations. They often work with structured data and use statistical techniques to conclude.
On the other hand, data scientists have a broader skill set and are involved in more complex tasks such as predictive modelling, machine learning, and algorithm development.
Business analysts, on the other hand, bridge the gap between business objectives and data analysis. They focus on understanding business requirements, identifying opportunities for improvement, and translating data insights into actionable strategies.
Challenges and opportunities in the field of data analysis
The field of data analysis presents both challenges and opportunities. One of the biggest challenges faced by data analysts is dealing with large and complex datasets. Analyzing vast amounts of data requires advanced analytical skills and the ability to work with different data formats.
Data privacy and security concerns also pose challenges, as data analysts need to ensure that sensitive information is handled securely. However, the growing demand for data analysts presents numerous opportunities.
With the increasing availability of data and advancements in technology, data analysts have the opportunity to work on diverse projects and contribute to strategic decision-making at all levels of an organization.
How to become a successful data analyst?
Becoming a successful data analyst requires a combination of education, relevant skills, and practical experience. A bachelor’s degree in a field such as mathematics, statistics, computer science, or economics is often preferred by employers.
However, having a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics is essential, regardless of the degree. It is also important to develop skills in programming languages such as Python or R, as well as data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI.
Practical experience gained through internships or real-world projects can significantly enhance your chances of landing a job as a data analyst.
Additionally, continuous learning and staying updated with the latest tools and techniques in data analysis are crucial for long-term success in this field.
Resources and courses for learning data analysis skills
There are numerous resources and courses available to help individuals learn and develop their data analysis skills. Online platforms such as Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer a wide range of courses on data analysis, statistics, and programming.
These courses cover topics such as data cleaning and preprocessing, statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
And if you are looking for a personalized training program, you must check our Data Science Course which includes all the modules and topics required to become a smart and skilled Data Analyst/Scientist.
Many of these platforms also offer specialized programs or certifications in data analysis, which can further enhance your credentials. Additionally, there are several books and online tutorials available that provide in-depth knowledge and practical examples of data analysis techniques.
Data Analyst Salary in India
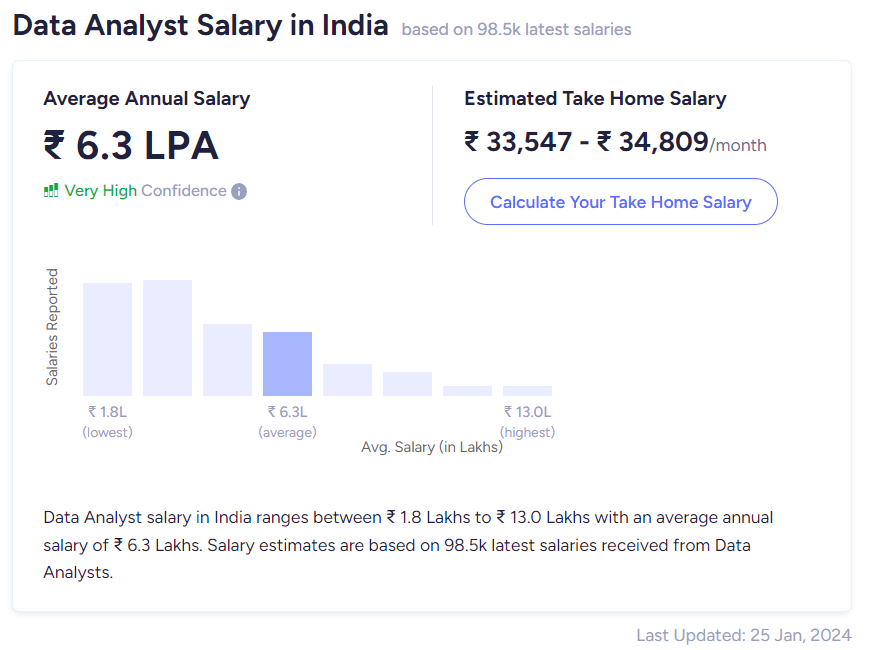
The salary of a data analyst in India can vary depending on factors such as experience, skills, location, and the industry they work in. According to recent data, the average salary of a data analyst in India ranges from INR 4-10 lakhs per annum. Some salary stats are listed below:
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range (₹ per annum) |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level (0-3 years) | ₹ 3,50,000 – ₹ 5,50,000 |
| Mid-Career (4-9 years) | ₹ 6,00,000 – ₹ 9,00,000 |
| Senior (10+ years) | ₹ 10,00,000 – ₹ 15,00,000 |
However, with experience and expertise, data analysts can earn significantly higher salaries. Industries such as IT, e-commerce, finance, and consulting tend to offer higher salaries for data analysts.
It is important to note that salaries may vary across different cities and regions in India. As the demand for skilled data analysts continues to grow, it is expected that the salaries in this field will also rise.
Conclusion
Data analysis plays a crucial role in helping businesses make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge. Data analysts are responsible for collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to extract meaningful insights.
To excel in this field, data analysts need to possess a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics, programming skills, and the ability to communicate effectively. Although the field of data analysis presents challenges, it also offers numerous opportunities for career growth and development.
By continuously learning and staying updated with the latest tools and techniques, aspiring data analysts can position themselves for success in this exciting field. So, join our data analyst training program today and embark on a rewarding career in data analysis.

13+ Yrs Experienced Career Counsellor & Skill Development Trainer | Educator | Digital & Content Strategist. Helping freshers and graduates make sound career choices through practical consultation. Guest faculty and Digital Marketing trainer working on building a skill development brand in Softspace Solutions. A passionate writer in core technical topics related to career growth.




