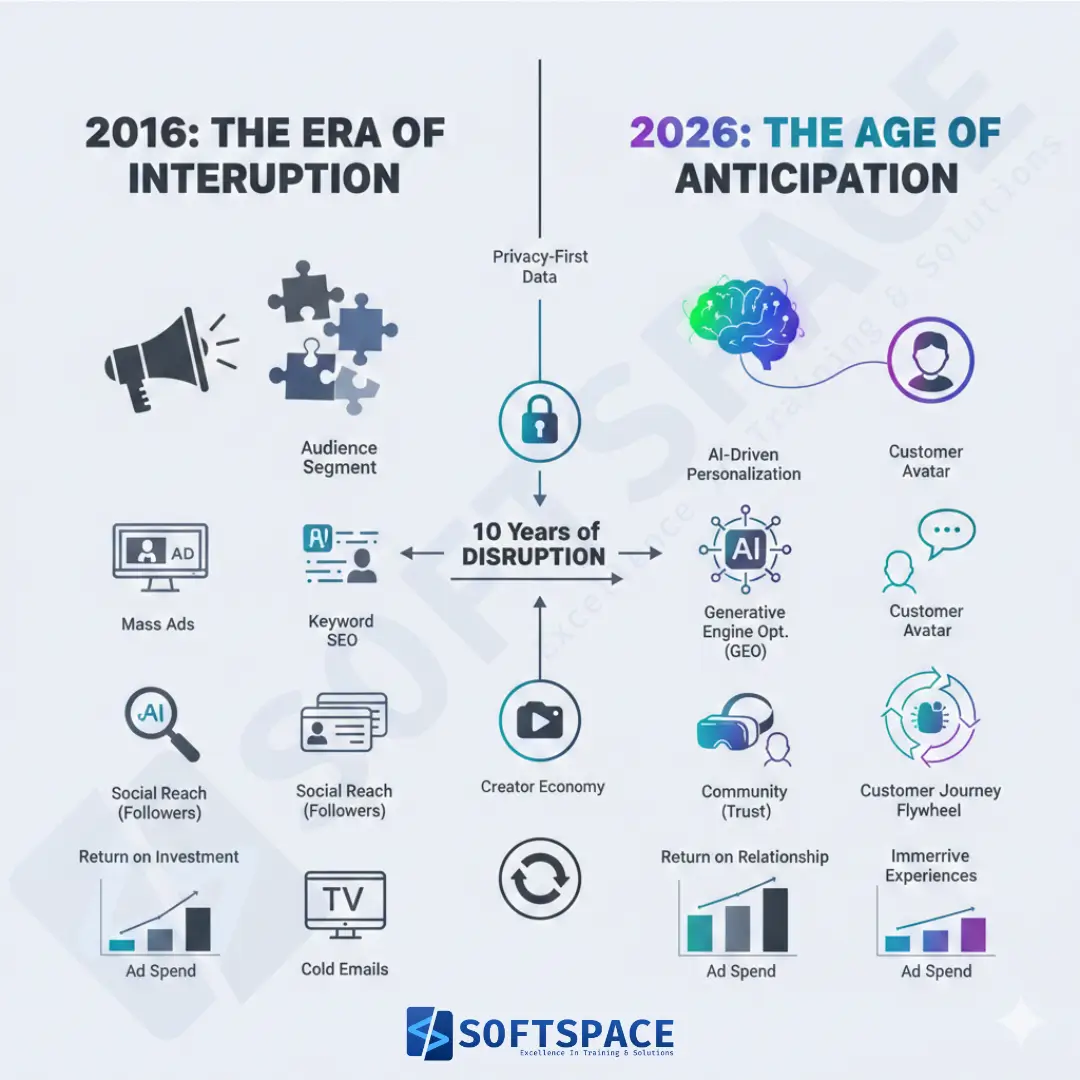
Marketing has changed in the last 10 years by shifting from interruption-based advertising and keyword SEO to AI-driven, privacy-first, trust-based marketing. Success now depends on Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO), zero-party data, AI agents, and building authority in AI-curated search environments.
In 2016, marketing was a game of interruption; in 2026, it is a game of intent. Over the last decade, we have moved from broad-reach television ads and keyword-stuffed blogs to a landscape where AI agents, privacy-first data, and “Answer Engines” define success.
Today, the question is no longer how to reach a customer, but how to become the most trusted authority in an AI-curated world. The question is how has marketing changed in the last 10 years? Is the death of the “click” as the primary metric?
Table of Contents
With 50% of Google searches now resulting in AI Overviews, brands are transitioning from SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) to GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation), optimising content to be the cited source in a chatbot’s answer rather than just a link on a page.
| Feature | Marketing in 2016 | Marketing in 2026 |
| Primary Search Goal | Rank #1 for Keywords | Be the cited source in AI Answers (GEO) |
| Data Backbone | Third-party cookies & tracking | First-party & Zero-party consent data |
| Content Strategy | “Viral” mass reach | Niche community & authentic UGC |
| Tech Focus | Automation tools | Autonomous AI Agents |
| Consumer Priority | Brand Awareness | Brand Trust & Ethical Transparency |
The Search Revolution: From “Ranking” to “Citability”
In 2016, a “first-page ranking” was the gold standard. Today, the landscape is dictated by AI Overviews (AIO) and Answer Engines. According to 2025 industry analyses by SparkToro and Similarweb, more than 50% of Google searches now result in zero-click outcomes, many driven by AI Overviews and direct answer formats.
1. What is GEO?
Generative Engine Optimisation is the practice of optimising content so that it is understood, trusted, and most importantly, cited by Large Language Models (LLMs) like Gemini, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. In 2026, appearing as a “suggested source” inside an AI answer is more valuable than being the first blue link below it.
2. The Strategy: Optimising for “Answer Engines”
To win in a GEO-driven world, your content must move beyond keyword density and focus on three pillars:
- Structured Data (Schema 3.0): AI doesn’t just “read” your site; it ingests your data. In 2026, advanced Schema markup is the digital architecture that tells AI exactly who your founders are, your real-time pricing, and your verified product specs.
- The “Information Gain” Requirement: If your blog post just summarises what is already on the web, AI will ignore it. Search engines now reward originality. This means including proprietary data, unique case studies, or “human-only” insights that an AI cannot replicate.
- Direct Answer Formatting: AI models look for “quotable” definitions. Use clear, unambiguous headers (e.g., “What is X?”) followed by a concise, factual 40-word summary.
2026 Pro-Tip: Statistics show that AI assistants cite brand websites only 5% to 10% of the time. The rest of their citations come from Reddit, niche forums, and review platforms. To rank, you must influence the conversation off your website as much as on it.
| Feature | Traditional SEO (2016) | Generative GEO (2026) |
| Primary Goal | Clicks to your website | Inclusion in AI Summaries |
| Key Metric | Keyword Position | AI Share of Voice & Citations |
| Content Type | Long-form articles (1,500+ words) | Structured, reusable data modules |
| Success Factor | Backlink volume | Factual accuracy & Authoritative data |
The Privacy-First Data Economy: Trust as the New Currency
If you asked how marketing has changed in the last 10 years regarding data, the answer is a total flip in power. In 2016, “Big Data” was about how much you could track without the user knowing. In 2026, data is about what the user chooses to tell you.
1. The Collapse of the Third-Party Cookie
The era of “stalking” ads, where a pair of shoes followed you across every website for weeks, is dead. Stricter global regulations (GDPR, CCPA, and the 2025 Privacy Acts) combined with Apple and Google’s technical lockdowns have made third-party cookies obsolete.
2. Zero-Party Data: The “Ask, Don’t Track” Model
The most valuable asset in 2026 is Zero-Party Data. This is information a customer intentionally and proactively shares with you.
- The 2016 Way: Inferring someone is a runner because they visited a sports blog.
- The 2026 Way: A customer completes a “Running Shoe Finder” quiz, telling you their arch type, weekly mileage, and favourite colour in exchange for a personalised recommendation.
3. The Value Exchange Strategy
In 2026, consumers know their data has monetary value. They won’t give it up for free. Brands that rank high in trust now use a Value Exchange model:
- Interactive Quizzes: “Find your perfect skincare routine.”
- Preference Centres: Letting users choose exactly what emails they get and how often.
- Gated Expert Tools: Access to a custom ROI calculator in exchange for a business email.
4. Data Privacy Comparison: 2016 vs. 2026
| Strategy | Traditional Tracking (2016) | Privacy-First Data (2026) |
| Collection | Hidden scripts & cookies | Direct quizzes, polls, & forms |
| User Perception | “Creepy” or intrusive | Helpful & personalised |
| Regulation | Minimal/Western-centric | Global compliance (GDPR/CCPA/EU AI Act) |
| Accuracy | Probabilistic (Guessed) | Deterministic (Stated by user) |
Trust-focused brands consistently outperform opaque competitors. A 2025 Edelman Trust Barometer report found that consumers are significantly more likely to purchase from brands they perceive as transparent and ethical.
Social Search & The Algorithmic Feed: The Death of the “Follower”
If you want to understand how marketing has changed in the last 10 years, look no further than your follower count. In 2016, a million followers was a guarantee of reach. In 2026, it is a vanity metric. We have moved from the Social Graph (who you know) to the Interest Graph (what you love).
1. The Rise of the Interest Graph
A decade ago, your feed was a chronological list of updates from friends and brands you followed. Today, platforms like TikTok and the evolved Instagram “For You” feeds use behavioural modelling to serve content.
- The 2016 Rule: You see content because you followed the account.
- The 2026 Rule: You see content because the algorithm knows you watched a similar video for more than 3 seconds.
Key Insight: This is “Democratic Reach.” In 2026, an account with zero followers can go viral globally overnight if the content resonates. Conversely, a brand with millions of followers can have a post reach fewer than 1,000 people if the engagement signals are weak.
2. Social Media is the New Search Engine
For Gen Z and Gen Alpha, the search journey no longer starts on a white screen with a search bar—it starts on social media. This shift to Social Search has turned captions and on-screen text into vital SEO real estate.
- Visual Discovery: Users search for “best quiet cafes in London” on TikTok to see the vibe, rather than reading a text-heavy list on a website.
- Social SEO (SSO): Marketers in 2026 optimise social posts using natural language keywords in captions, hashtags, and even spoken audio, as algorithms now transcribe video in real-time to index content for search.
3. Community Over Clout: The “Private” Shift
As public feeds become more crowded with AI-generated noise, users are retreating into “Digital Campfires”, smaller, private communities where trust is higher.
- Owned Communities: Brands are moving away from “rented” social reach and building owned spaces on Discord, WhatsApp Channels, and private Slack groups.
- Micro-Trust: A recommendation in a private community of 500 people is 10x more likely to convert than a public ad seen by 500,000.
Comparison: The 10-Year Social Evolution
| Strategy | Social Media in 2016 | Social Media in 2026 |
| Reach Driver | Follower Count | Content Engagement & Watch Time |
| Primary Metric | Likes & Impressions | Saves, Shares, & “Time Spent” |
| Discovery | Word of Mouth / Follows | Algorithmic “For You” Feeds |
| Content Style | Polished & Curated | Raw, Lo-fi, & “Human” |
The AI Infrastructure: From “Automated” to “Autonomous”
If you want to know how marketing has changed in the last 10 years, look at the role of the marketer. In 2016, marketers used AI to help them write; in 2026, marketers use AI Agents to help them execute. We have transitioned from “if-this-then-that” rules to goal-oriented systems that think and act independently.
1. The Rise of the AI Marketing Agent
Ten years ago, “marketing automation” meant a pre-set email sequence. Today, we use Autonomous Agents. These aren’t just tools; they are “digital employees” capable of planning and optimising entire campaigns with minimal human oversight.
- The 2016 Method: A human manually sets a bid for a keyword and checks it 48 hours later.
- The 2026 Reality: An AI agent monitors your CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) in real-time across six platforms, reallocating budget and swapping ad creatives every 60 seconds to hit a specific revenue goal.
2. Hyper-Personalisation: The “Anticipation” Era
We have moved past “Hi [First Name]” into Anticipatory Marketing. By 2026, AI will have graduated from pattern matching to complex reasoning.
- Generative UI (GenUI): Interfaces now “morph” in real-time. If an AI agent detects a user is browsing for “high-altitude hiking boots,” the website doesn’t just show a product grid; it dynamically reorganises the entire homepage into a personalised “Expedition Portal” featuring socks, crampons, and weather-appropriate gear.
- Contextual Intelligence: AI now uses real-time signals—like the user’s local weather, time of day, or even biometric stress levels (with consent)—to adjust the tone of a message.
3. “Share of Model”: The New KPI
In the last decade, we fought for “Share of Voice.” In 2026, the primary metric for top-tier brands is Share of Model.
Key Insight: As more consumers use personal AI assistants to shop for them (e.g., “Find me the best eco-friendly espresso machine under $500”), your goal is to ensure your brand is the one the AI assistant recommends. If you aren’t in the LLM’s training data or cited in its “Answer Engine,” you don’t exist to the 2026 consumer.
4. Comparison: Automation (2016) vs. Autonomy (2026)
| Feature | Marketing Automation (2016) | Autonomous Marketing (2026) |
| Logic | Rigid, rule-based (workflows) | Goal-oriented (agents) |
| Speed | Reactive (daily/weekly updates) | Proactive (real-time/instant) |
| Personalization | Segments (Group-based) | Individualised (1-to-1) |
| Human Role | Task execution & setup | Strategy, Ethics, & “Agent Architect” |
This section addresses the physical evolution of the digital world. In 2026, “mobile-first” has been replaced by “Spatial-First.”
VI. Immersive Commerce: The Spatial Shift
When asking how has marketing changed in the last 10 years, the most visible answer is the transition from 2D screens to 3D environments. In 2016, Augmented Reality (AR) was a gimmick used for catching virtual monsters (Pokémon GO). In 2026, Spatial Commerce is a core conversion engine that has fundamentally solved the “uncertainty gap” in online shopping.
1. The Death of the 2D Product Page
Ten years ago, a “good” product page had five high-res photos and a video. Today, that is considered static and uninformative.
- The 2016 Method: Zooming in on a JPEG to guess the texture of a sofa.
- The 2026 Reality: Using a headset or smartphone to “place” a true-to-scale 3D model of that sofa in your actual living room.
The “Conversion Jump”: Shopify’s 3D commerce report found that merchants using AR product previews saw conversion rate increases of up to 94% compared to static imagery.
2. Reducing the “Return Crisis”
One of the biggest marketing headaches of the last decade was the skyrocketing rate of e-commerce returns. Spatial marketing has become the primary solution.
- Virtual Fitting Rooms: AI-powered body scanning allows customers to “wear” clothing digitally with 99% accuracy in fit.
- Result: Retailers utilising AR try-ons report a 25-30% drop in return rates, as customers no longer have to buy three sizes to find one that fits.
3. From Impressions to “Experiences”
In the 2016 era, we tracked “Impressions”—how many people saw an ad. In 2026, we track Spatial Engagement.
- Mixed Reality Ads: Instead of a banner ad, a brand might drop a “spatial portal” in a city centre (accessible via glasses or phone) where users can interact with a 3D brand story.
- The Metric: “Time Spent in Experience” is now more valuable than a click, as it signals a deeper emotional and cognitive connection with the brand.
4. Comparison: The 10-Year Gear Shift
| Metric/Feature | Digital Marketing (2016) | Spatial Marketing (2026) |
| Primary Interface | Smartphone / Desktop (2D) | Smart Glasses / Mixed Reality (3D) |
| Consumer Action | Clicking & Scrolling | Gesturing & Interacting |
| Success Metric | Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Engagement Depth & Scale Accuracy |
| Shopping Hub | Marketplaces (Amazon/Web) | Immersive Environments (The Home/Metaverse) |
This section addresses the “Human Element”—the only part of marketing that AI cannot replicate. In 2026, trust is the scarcest resource, and ethical transparency is the only way to earn it.
The “Human-Only” Moat: Ethics, Truth, and Radical Transparency
In the last decade, we have moved from an era of “perfect” brand images to an era of “Radical Honesty.” In 2016, a brand could hide behind a polished PR statement. In 2026, with the rise of deepfakes and AI-generated noise, consumers assume they are being misled until proven otherwise.
1. Authenticity as a Security Requirement
The threat landscape has changed. In 2026, deepfakes are involved in over 30% of high-impact corporate impersonation attacks. To combat this, marketing has become a verification game.
- Content Provenance: Top brands now embed cryptographic “digital signatures” in their videos and images to prove they are official and unmanipulated.
- HITL is a necessity: According to a 2025 Originality.ai study analysing millions of pages, a significant percentage of newly published web content shows detectable AI assistance.
2. Sustainability: From “Buzzword” to “Table Stakes”
Ten years ago, “going green” was a niche marketing angle. Today, it is an economic necessity.
- The 2016 Method: “Greenwashing” with vague claims like eco-friendly or natural.
- The 2026 Reality: Digital Product Passports (DPPs). Consumers now scan a QR code on a product to see its entire supply chain—from the carbon footprint of the factory to the fair-wage certification of the workers.
- Gen Alpha Influence: 64% of Gen Z and Gen Alpha consumers report they will stop purchasing from a brand linked to unethical suppliers.
3. The Paradox of AI Trust
Ironically, as we use more AI to scale, consumers want more imperfection.
- Vulnerability Marketing: Brands like Ace & Tate have seen massive success by admitting their flaws (e.g., publicly sharing where they failed to meet sustainability goals).
- The Goal: Don’t be “AI-Perfect”; be “Human-Imperfect.” This builds a deeper emotional connection that no algorithm can disrupt.
4. Comparison: The Ethical Shift (2016 vs. 2026)
| Feature | Corporate Marketing (2016) | Ethical Marketing (2026) |
| Messaging | Polished & Curated | Radically Honest & Vulnerable |
| Sustainability | Marketing Claim (Optional) | Verified Data (Mandatory) |
| AI Policy | Hidden/Automated | Transparent & Human-Vetted |
| Data Usage | Exploitative/Hidden | Consent-Based & Reciprocal |
Conclusion: The Roadmap for the Next Decade
When we look at how marketing has changed in the last 10 years, we see a clear trajectory: we have moved from chasing the “Algorithm” to serving the “Individual.” The brands that are thriving in 2026 are those that have successfully integrated AI efficiency with human empathy.
To survive the next ten years, your marketing department must shift from being a “Content Factory” to an “Experience Architect.“
Your 2026 Marketing Audit Checklist
To stay ahead of the curve, every brand should perform these three critical checks today:
- The GEO Audit: Search for your brand in an AI Answer Engine (like Gemini or SearchGPT). Is the AI citing your website as a source of truth, or is it pulling from a competitor? If you aren’t being cited, your Schema Markup and Information Gain need immediate attention.
- The Data Value Exchange: Review your lead magnets. Are you still asking for an email in exchange for a generic PDF? Swap it for a high-value Zero-Party Data tool, such as a personalised AI calculator or an interactive diagnostic quiz.
- The Human-in-the-Loop Policy: Establish a public-facing policy on how you use AI. Transparency about which parts of your content are AI-generated and which are human-vetted is now a primary driver of brand trust.
Final Thoughts: Innovation is the Only Constant
The last decade proved that “safe” marketing is the riskiest strategy. In 2016, we feared the decline of organic reach; today, we embrace the power of algorithmic discovery. In 2016, we worried about ad-blockers; today, we build immersive experiences that people want to interact with.
The future of marketing belongs to the agile. By understanding these shifts and prioritising genuine connections over sheer volume, your business can secure its place in the ever-evolving marketplace of 2026 and beyond.
FAQs
How has marketing changed in the last 10 years?
Marketing has shifted from interruption-based advertising and keyword-driven SEO to AI-powered, intent-based discovery. Over the past decade, brands have moved toward privacy-first data, Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO), social search, immersive commerce, and trust-led transparency to remain visible in AI-curated environments.
What is the biggest change in digital marketing since 2016?
The biggest change in digital marketing since 2016 is the decline of the click as the primary metric. With the rise of AI Overviews, zero-click searches, and answer engines, success now depends on being cited inside AI-generated summaries rather than simply ranking first in search results.
How has AI changed marketing strategies?
AI has transformed marketing from automation to autonomy. Instead of rule-based workflows, brands now use AI agents to optimise budgets, personalise content in real time, predict customer intent, and dynamically adapt user experiences across channels.
Is SEO still relevant in 2026?
Yes, but it has evolved. Traditional SEO focused on keyword rankings and backlinks. In 2026, Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) prioritises structured data, factual accuracy, and authoritative content so that AI systems cite your brand in search summaries and assistant responses.
Why are third-party cookies disappearing?
Third-party cookies are being phased out due to global privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, along with browser-level restrictions from Apple and Google. Brands are replacing them with first-party and zero-party data collected transparently through quizzes, preference centres, and value exchanges.
What is zero-party data in marketing?
Zero-party data is information that customers intentionally share with a brand, such as preferences, goals, or purchase intent. Unlike inferred tracking data, zero-party data is consent-based, accurate, and aligned with privacy-first marketing strategies.
How has social media marketing evolved?
Social media has shifted from follower-based reach to algorithm-driven discovery. Platforms now prioritise watch time, saves, and engagement signals over follower count, enabling smaller creators and brands to achieve global visibility through interest-based feeds.
What is Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) is the practice of structuring content so it is cited by AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. It focuses on factual clarity, structured data, originality, and demonstrable authority rather than traditional keyword density.
Research & Industry Sources Referenced
- SparkToro – Zero-Click Search Study: https://sparktoro.com/blog/less-than-half-of-google-searches-now-result-in-a-click/
- Shopify – 3D Commerce / AR Report: https://www.shopify.com/blog/augmented-reality-ecommerce
- Edelman – Trust Barometer 2025: https://www.edelman.com/trust/2025/trust-barometer
- Gartner – AI in Marketing Research: https://www.gartner.com/en/marketing/insights/artificial-intelligence
- McKinsey – State of AI Report: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai

Content Strategist | AI Tools Practitioner | Career & Study Abroad Consultant
Sagar Hedau is a content strategist and AI tools practitioner based in Nagpur, India. With 13+ years of experience in career counselling and psychometry, he now works at the intersection of content strategy and no-code AI technology, using tools like Claude, Lovable, LovArt, and Notion AI in his daily workflow. He writes to make AI genuinely accessible for non-technical professionals, students, and business owners who want to build and automate without coding. He also runs an active career counselling practice, helping individuals navigate career decisions with data-backed psychometric analysis.
🌐 sagarhedau.com | 💼 LinkedIn

