The first and most important step in getting your material found is to get it indexed on Google. Without indexing, the 13.6 billion queries that take place on the most popular search engine in the world each day would not be able to see even the best information.
The indexing environment has changed significantly in 2026. Google currently uses mobile-first algorithms, AI-enhanced crawlers, and advanced quality filters to process material and decide which pages should be included in the index and which should be excluded.
Knowing how to effectively get indexed on Google has never been more important, as recent statistics indicate that just 64.86% of new pages are indexed during the first 30 days, and 96.55% of indexed pages generate zero traffic.
This thorough book explains the most recent tactics, data, and technological specifications to guarantee that your material is swiftly indexed and stays visible in Google’s search results until 2026 and beyond.
Get Indexed on Google in 2026: What’s Changed?
Understanding how indexing functions in the current AI-driven search landscape is crucial before launching into strategies to get indexed on Google.
Table of Contents
Get Indexed on Google. How and Why?
The process by which Googlebot visits your webpages, examines their content, and adds them to Google’s enormous search database, the index, is known as Google indexing. Search results can only show pages that have been indexed.
Consider it like adding books to a library catalogue: regardless of how good your material may be, searchers won’t be able to find your page if it isn’t catalogued (indexed).
Over 100 million terabytes of material are currently included in Google’s index, but the search engine has gotten more picky about what it displays. Indexing rates significantly decreased in 2022 and 2023 as Google battled the rise in AI-generated content, which was a major change from previous years.
However, as Google’s systems developed and content producers adjusted to quality criteria, there was a proportionate increase in indexed pages in 2024 and 2025.
Google Indexing’s Present Situation: 2026 Data
Setting reasonable expectations when trying to get indexed on Google is made easier by being aware of the current indexing environment:
Indexing Rates of Success and Speed:
- The average time for pages to be indexed by Google is 27.4 days.
- Just 14% of pages are indexed within the first week
- 64.86% within 30 days
- 76.81% within three months
- 93.2% of pages are indexed within six months.
Indexing Difficulties:
- Over 50% of websites have trouble being indexed by Google, frequently as a result of poor quality.
- Of all indexed pages, 96.55% get no organic traffic.
- Ten visits or fewer are received by just 1.94% of indexed pages per month.
- De-indexing eventually affects 21.29% of indexed pages, with 13.7% being deleted in three months.
Reality First on Mobile Devices:
- More than 70% of websites have switched to mobile-first indexing.
- Mobile devices now account for 62–64% of all website traffic worldwide.
- Sites that are optimised for mobile devices have a 67% higher chance of appearing on Google’s first page.
- Websites lacking mobile optimisation risk de-indexing and severe ranking penalties.
These figures make it very evident that producing content alone is insufficient. In 2026, obtaining Google indexation requires a methodical and technically sound approach.
Why Google Doesn’t Index Pages?
Determine the typical barriers stopping pages from being indexed before putting remedies in place:
Problems with Quality and Value
Low-quality pages won’t be indexed because of Google’s Helpful Content Updates and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) standards. Google rejects pages that include duplicate material, AI-generated fluff, or thin content.
Technical Difficulties
- Robots.txt blocking: Googlebot access is blocked by inadvertent disallow rules
- Meta robots tags that specifically tell Google not to index are known as noindex tags.
- 5xx problems are server faults that prevent pages from being accessed during crawl efforts.
- Slow loading times: Crawl priority is reduced for pages with subpar Core Web Vitals.
Issues with Discoverability
What Google cannot find, it cannot index. Crawlers are unable to see pages that are buried deep inside the site architecture without internal links or sitemap inclusion.
Content Duplication
When multiple URLs include material that is identical or significantly similar, Google only indexes the canonical version; duplicates are not included in the index.
Problems with Mobile Usability
Pages that aren’t mobile-friendly risk significant indexing difficulties and possible deletion from search results once Google fully switches to mobile-first indexing by July 2024.
What issues did we face recently?
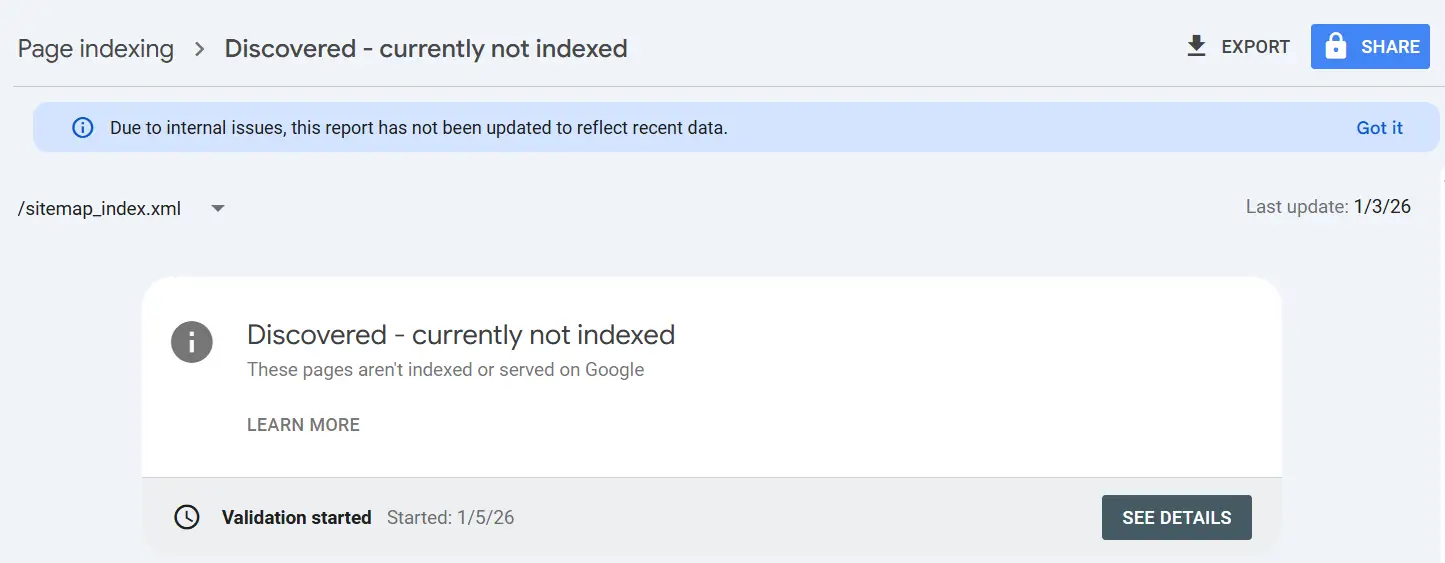
In RankMath, the sitemap is divided into pages, posts and categories. We faced an https indexing issue with posts, and we had to resubmit the posts’ sitemap again to resolve it.
How to Get Indexed on Google: Crucial Technical Configuration
Step 1: Use Google Search Console to confirm your website
The most effective tool for assisting you in becoming indexed on Google is Google Search Console (GSC), which is your direct line of communication with Google.
Procedure for Setting Up:
- Go to the Google Search Console.
- Add your property (for thorough coverage across all subdomains, select Domain).
- Use the tag approach, HTML file upload, or DNS to confirm ownership.
- For more in-depth information, go to Google Analytics 4.
Step 2: Make an XML sitemap and submit it
An XML sitemap serves as a roadmap, displaying to Google all of the key URLs you would like crawled.
2026 Sitemap Best Practices:
- Only canonical URLs should be included; do not include duplicates.
- Limit each sitemap to 50 MB uncompressed or 50,000 URLs.
- When new content is published, it updates automatically.
- Get rid of 404 pages and URL redirects.
- Set the appropriate priority values for key pages.
- Use Google Search Console’s “Sitemaps” section to submit a sitemap.
Sitemaps for WordPress websites are automatically created and updated by plugins such as Yoast SEO, RankMath, or All in One SEO. Screaming Frog SEO Spider and XML-Sitemaps.com are two programs that can generate sitemaps from your URL structure for other platforms.
Step 3: Optimise Your Robots.txt File
Your robots.txt file controls which parts of your website are accessible to the search engines.
Critical Robots.txt Guidelines:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /private/
Sitemap: https://yoursite.com/sitemap.xmlAvoid these common mistakes of errors
- Never inadvertently block your entire website or key areas.
- Avoid blocking JavaScript or CSS files, as Google need them for mobile-first indexing.
- Use the robots.txt Tester in Google Search Console to confirm rules. Keep in mind that robots.txt is a recommendation, not security; use noindex meta tags for content that you do not want indexed at all.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Mobile-First Indexing
Your mobile version affects indexing success because mobile-first indexing is now applied to 100% of websites.
Checklist for Mobile Optimisation:
- A single URL providing content that is optimised for all devices is known as responsive design.
- Configuring the viewport: The appropriate meta viewport tag
- Text that can be read: font size of at least 16 pixels without horizontal scrolling
- Touch-friendly components: Tap targets with a minimum of 48 by 48 pixels and sufficient spacing
- Fast loading: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) should load in less than 2.5 seconds.
- The main content of the desktop and mobile versions is identical.
- Structured data: The mobile version has schema markup.
To find and address mobile problems that might be impeding successful indexing, use Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability report.
While doing all these implementations, avoid these common mistakes in SEO to stay ahead and safe.
Advanced Techniques for Quicker Google Indexing
Method 1: Use the URL Inspection Tool to Request Indexing
To speed up the process, manually request indexing for newly added or changed pages.
How to Make an Indexing Request:
- Launch the Google Search Console.
- In the upper search bar, type your URL.
- Click “Request Indexing” if the page displays outdated content or isn’t indexed.
- Requests are normally processed by Google in 1-2 days, though this is not always the case.
Significant Limitation: Make strategic use of this; Google restricts indexing queries, so instead of sending every URL, focus on your most significant pages.
Method 2: Use Social Signals
Social media may speed up indexing discovery, according to recent research.
Method for Accelerating Social Indexing:
- Release your fresh material.
- Post the URL on active social media sites like X.com (previously Twitter).
- Give the link some context.
- After publishing, click the link yourself.
This alerts Google to the presence of third-party traffic to your URL.
Because it establishes an external discovery channel that goes beyond conventional crawling, this approach is effective.
Method 3: Establish Strategic Internal Connections
One of the most effective yet underutilised strategies for assisting new pages in Google indexation is internal linking.
Best Practices for Internal Links:
- Link to new pages from high-authority, already-indexed pages
- Make use of informative anchor text to convey the page’s subject.
- When applicable, provide links from your main navigation or homepage.
- Contextual links should be made within related content.
- Create a site architecture that makes sense and has distinct hierarchies.
- Make sure the homepage is only three to four clicks away from every page.
By following links from well-known pages, Google finds new pages. Robust internal linking guarantees that Googlebot will rapidly locate your content and recognise its significance within the structure of your website.
Method 4: Obtain High-Quality Backlinks
External links from reputable websites have two functions: they convey the worth of your content and aid Google in finding it.
Creating Links in 2026 for Indexing:
- Write guest posts for reputable websites in your field.
- Become highlighted in trade journals and news websites
- Send your work to reputable, pertinent directories (such as Crunchbase for businesses).
- Make resources that are easy to distribute and will inevitably generate links.
- Develop connections with influential people in the sector
- Steer clear of paid link schemes, link swaps, and private blog networks (PBNs).
Backlinks are still the third most important ranking criterion and continue to speed up discovery and indexing, even though their weighting in Google’s algorithm decreased from 15% to 13%.
Optimising Content for Google Indexation
Produce Excellent, Indexable Content
Google’s Helpful Content Update from September 2023 reaffirmed how quality evaluation driven by AI now significantly affects indexing choices.
Criteria for Content Quality:
- Length and depth: For in-depth subjects, aim for 1,500+ words.
- Originality: Distinct viewpoints supported by knowledge and experience
- E-E-A-T signals: Exhibit Knowledge, Proficiency, Credibility, and Authority
- Cited sources: Consult research, data, and reliable sources.
- Structured format: Make use of lists, logical organisation, and distinct headings (H2, H3).
- Multimedia components: Add unique pictures, movies, charts, and infographics.
- Value to the user: Address real issues and provide real answers.
According to studies, information that uses data, cited sources, and authoritative language can raise its search engine ranks by 89–134%. These findings also hold for traditional indexing.
Use Schema Markup to Implement Structured Data
Schema markup improves indexing efficiency and the possibility of rich results by assisting Google in understanding the context of your content.
Schema Types of Priority for 2026:
- Article structure: For news articles and blog entries
- Product schema: For online stores
- Local Business Schema: For companies with a physical location
- For often asked questions, use the FAQ format.
- How-to schema: For educational materials
- Review schema: For evaluations of goods and services
Before publishing, use Google’s Rich Results Test tool to verify markup and use JSON-LD format, which is Google’s recommended format.
Enhance the Essential Web Elements
In Google’s mobile-first ecosystem, Core Web Vitals have a direct impact on indexing priority and crawl efficiency.
Core Web Vitals Objectives for 2026:
- Less than 2.5 seconds is the largest contentful paint (LCP).
- Interaction with Next Paint (INP): Less than 200 ms
- CLS (cumulative layout shift): less than 0.1
Strategies for Optimisation:
- Images should be optimised and compressed using the WebP format.
- Use lazy loading for pictures that are below the fold.
- Reduce the amount of CSS and JavaScript
- Make good use of browser caching
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) activation
- Improve the response time of the server.
- Render-blocking resources should be removed.
While weak performers risk delays and possible exclusion, pages with strong Core Web Vitals earn larger crawl budgets and quicker indexing.
Monitor and Troubleshoot Indexing Issues
Use Google Search Console’s Index Coverage Report
The Page Indexing report (formerly Index Coverage) reveals which pages Google has indexed and identifies problems preventing indexing.
| Report type | Description |
|---|---|
| Indexed pages | Successfully added to Google’s index |
| Not indexed | Pages Google chose not to index with specific reasons |
| Crawled – currently not indexed | Pages Google found but didn’t consider valuable enough |
| Discovered – currently not indexed | URLs Google knows about but hasn’t crawled |
Common Indexing Issues and Fixes
| Status | Issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “Crawled – currently not indexed” | Google crawled the page but didn’t index it due to perceived low quality | Improve content depth, add unique value, enhance E-E-A-T signals |
| “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” | Multiple similar pages exist without a clear canonical designation | Add canonical tags pointing to your preferred version |
| “Blocked by robots.txt” | The Robots.txt file prevents Googlebot access | Remove or modify the blocking rule in robots.txt |
| “Soft 404” | Page returns 200 status but contains little meaningful content | Add substantial content or return a proper 404 status for truly missing pages |
| “Server error (5xx)” | The server was unavailable during a crawl attempt | Investigate server stability and hosting capacity |
Weekly monitoring tasks:
- Check the Index Coverage report for new errors
- Review the Search Console Performance tab for sudden drops
- Monitor Core Web Vitals for degradation
- Track sitemap submission status
- Check for manual actions or security issues
Getting Used to AI Overviews and the Search Environment in 2026
Recognising the Effects of AI Overviews on Indexing Strategy
About 16% of enquiries now display Google’s AI Overviews (previously Search Generative Experience), adding a new layer of visibility above conventional organic results.
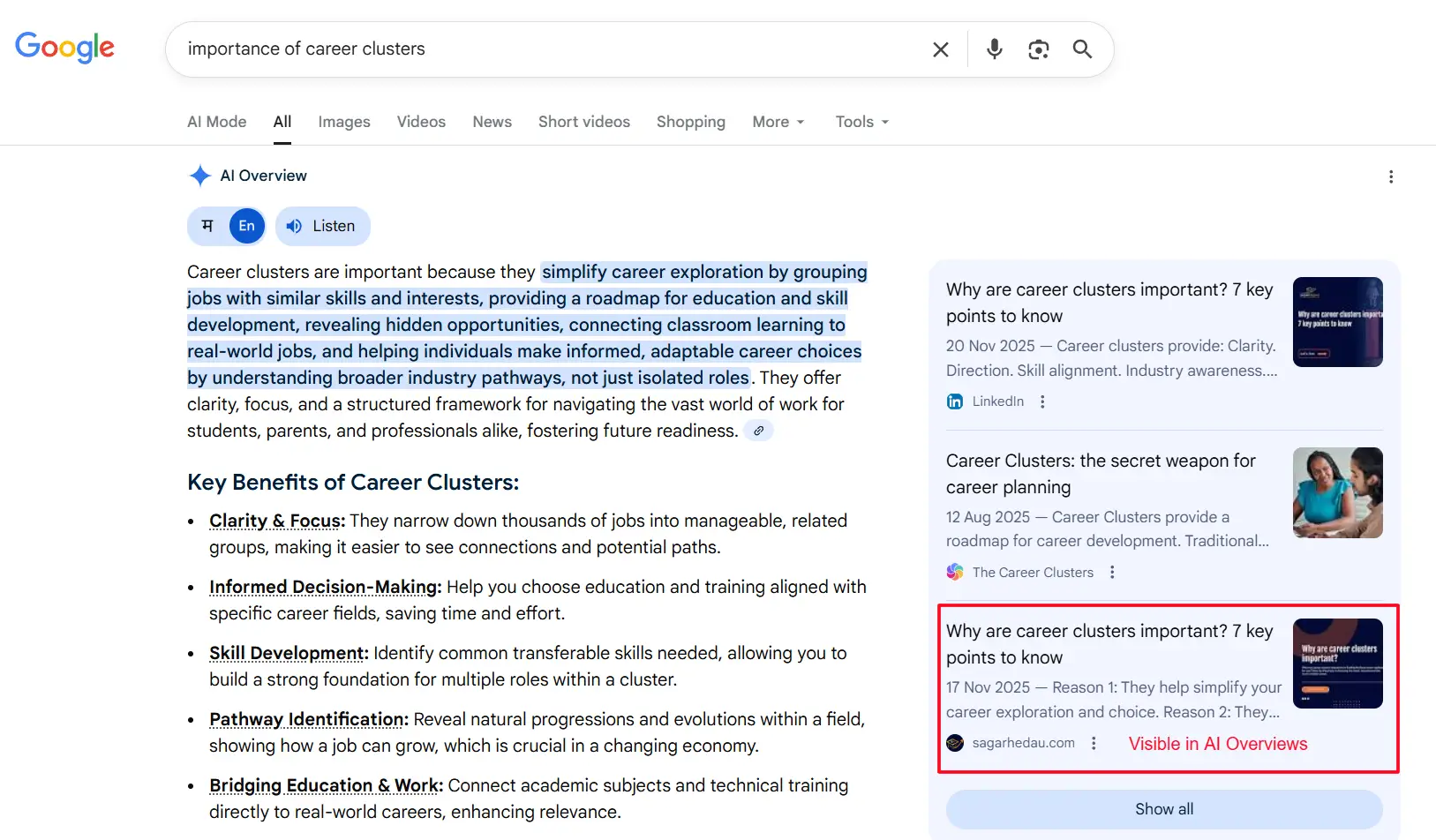
Statistics for AI Overviews:
- 38.7% of the time, informational enquiries display AI Overviews.
- AI Overviews appear on 25.96% of keywords in the science sector.
- In May 2024, zero-click searches rose from 56% to 69% in May 2025.
- The average CTR decrease for pages that appear in AI Overviews is 34.5%.
Implications for Indexing: Google indexing is still crucial, but visibility now goes beyond the index to include citations in AI-generated responses. Both AI systems that synthesise information and conventional indexing needs must be met by the content.
Optimising for AI Citations as Well as Conventional Indexing
Dual-Optimisation Approach:
- Keep up the basics of SEO: Authority-building, technical mastery, and high-quality content are still crucial.
- Framework for understanding AI: Explicit responses, logical structure, and distinct headings
- Create indications of authority: The probability of an AI citation is increased by high E-E-A-T scores.
- Make multimedia resources: Infographics, movies, and pictures offer more indexing pathways.
- Pay attention to entity relationships: Aid AI systems in comprehending the connections between your material and more general subjects.
The firms that are successful in 2026 understand that retaining traditional rankings and obtaining AI citations require continuous content excellence, but getting indexed on Google is the cornerstone.
Re-indexing and Content Freshness
Updating to Maintain Indexed Status
It needs constant effort to get your site indexed; getting indexed once isn’t enough.
Strategies for Content Freshness:
- Every six to twelve months, update the current content.
- Include up-to-date data, examples, and fresh statistics.
- Extend thin content to satisfy quality standards
- Resolve obsolete references and broken links.
- After major revisions, request re-indexing
Re-Indexing Procedure:
- Make significant content enhancements
- If necessary, change the published date.
- To request re-indexing, use the URL Inspection tool.
- Check the Index Coverage report to make sure.
According to recent data, 13.7% of indexed pages are removed within three months after first indexing, and 21.29% of indexed pages eventually suffer de-indexing. Maintaining indexed status and avoiding removal are made easier with frequent updates and quality enhancements.
Recognising the Dangers of De-Indexing
Warning Indications That Your Pages Could Be De-Indexed
- Unexpected decreases in traffic without a tie to algorithm updates
- Pages in the Index Coverage report are going missing.
- Site: Some URLs are no longer displayed in searches
- An increase in the number of “Crawled – currently not indexed” categories
Check impacted pages for quality concerns, technical issues, or policy infractions as soon as you see these indicators.
Developing a Long-Term Indexing Plan for 2026
Developing an Indexing-Friendly Website Architecture
- Reduce the number of clicks from the homepage to any page with a flat site structure.
- logical hierarchy of categories
- Navigation using breadcrumbs
- HTML and XML sitemaps
- Handling pagination with “View All” or rel=”next” and rel=”prev” pages
- Clearly defined URL structure with pathways that are rich in keywords and descriptive
Creating a Rhythm for Content Publishing
At 14% weighting, consistently producing satisfactory material continues to be the top-ranking factor in Google’s algorithm.
Publishing Plan for Indexing Achievement:
- Set up a consistent publishing schedule (monthly, biweekly, or weekly).
- Give quality precedence over quantity.
- Along with new creations, update current content.
- Cover subjects in-depth that fall under your area of expertise.
- Create content clusters to increase topical authority.
- Keep an eye on what is quickly indexed and duplicate those traits.
Making Sensible Use of AI Tools
Although they can speed up production, AI content-generating tools must be handled cautiously to guarantee proper indexing.
Guidelines for Indexing AI Content:
- AI should be used for research, drafting, and sketching, not for final products.
- Include firsthand knowledge, original ideas, and professional analysis.
- Check all of the data and facts.
- Edit extensively to ensure originality and quality.
- AI content should never be published without substantial human improvement.
- Give “helpful content written by people, for people” (Google’s standard) top priority.
Pages with the majority of the primary material produced by AI or auto-generation without significant human input now receive “Lowest” ratings from Google’s quality raters. Indexing pure AI stuff is quite difficult.
Advanced Troubleshooting: When Pages Fail to Be Indexed
The Issue of “Crawled – Not Indexed”
In 2026, this has emerged as one of the most annoying indexing problems.
Steps for Deep Troubleshooting:
- Audit of content quality: Contrast with leading rivals
- Verify that the material on your website is unique by checking for duplicates.
- Value assessment: Does this site provide a better solution than the current findings?
- Internal links: Increase the number of contextual links from pages with high authority.
- Obtaining backlinks: Obtain a minimum of one high-quality external connection
- Use the appropriate schema markup for structured data.
- Expand your content by adding at least 500 additional words of insightful material.
- Additional multimedia: Add original pictures, infographics, or videos
- Patience: After three to six months of achieving quality standards, pages may be indexed.
When to Take Noindex Into Account
Not every page should or should be included in Google’s index.
Pages to Think About Without Indexing:
- Minimal thank-you notes
- Account/login pages
- Checkout pages and shopping carts
- Results pages for internal searches
- Duplicate content (if there is a preferable version, use canonical instead)
- Low-value category and tag pages
- Pages for testing or staging
By avoiding crawl budget waste on low-value pages, strategic noindexing enables Google to concentrate on information that ought to be indexed.
Typical Myths About Indexing Disproved
The First Myth: “Every page on my site should be indexed”
Quality is more important than quantity in reality. Google favours websites with fewer high-quality indexed pages over those with a large number of low-value pages.
Myth two: “Paid advertising helps pages get indexed faster”
The truth is that organic indexing and Google Ads function separately. Indexing speed is unaffected by paid advertisements.
Myth number three: “Social media shares directly impact indexing”
Reality: Social signals aren’t direct ranking or indexing elements, but they do aid in discovery. They make it easier for Google to locate material.
Myth number four: “Submitting to search engines guarantees indexing”
In actuality, a submission asks for indexing consideration rather than a guarantee of indexing. Technical and quality standards still need to be fulfilled.
Myth number five: “More keywords in content help indexing”
The truth is that keyword stuffing degrades indexing prospects and user experience. Content that is useful and natural performs better.
Conclusion: How to Get Indexed on Google Easily and Successfully in 2026
A multifaceted strategy combining technical prowess, superior content, mobile optimisation, and strategic site architecture is needed to get indexed on Google in 2026. It is no longer sufficient to just post material and hope that it will be automatically indexed.
- Submit a comprehensive XML sitemap
- Optimise robots.txt file
- Ensure mobile-first compliance
- Implement responsive design
- Optimise Core Web Vitals
- Create original, high-quality content (1,500+ words)
- Build a strategic internal link structure
- Acquire quality backlinks
- Add structured data markup
- Request indexing for priority pages
- Monitor Index Coverage reports weekly
- Update content regularly
- Fix technical errors promptly
- Build topical authority in your niche
Getting indexed by Google is a continuous process rather than a one-time accomplishment. The search landscape is changing as a result of Google’s algorithms, mobile-first standards, and AI integration. Brands that remain flexible, put quality first, and uphold technological superiority are the ones that prosper.
Keep in mind that although visibility dynamics are shifting due to AI Overviews and zero-click searches, the fundamentals are still the same: you need to be indexed on Google before you can compete for any kind of visibility, either AI-generated citations or traditional organic results.
Put these tactics into practice right now, keep a regular eye on your outcomes, and adjust as Google’s needs change. Make sure your content receives the indexed foundation required for search success in 2026 and beyond, since it deserves to be found.

Content Strategist | AI Tools Practitioner | Career & Study Abroad Consultant
Sagar Hedau is a content strategist and AI tools practitioner based in Nagpur, India. With 13+ years of experience in career counselling and psychometry, he now works at the intersection of content strategy and no-code AI technology, using tools like Claude, Lovable, LovArt, and Notion AI in his daily workflow. He writes to make AI genuinely accessible for non-technical professionals, students, and business owners who want to build and automate without coding. He also runs an active career counselling practice, helping individuals navigate career decisions with data-backed psychometric analysis.
🌐 sagarhedau.com | 💼 LinkedIn

